In 2025, the question of how to know if a picture is fake matters to everyone. It’s common to run into a false payment receipt, a post about crypto using edited screenshots, or even manipulated product photos tied to Etsy scams. Research on arXiv reports that more than 40% of verified online misinformation is linked to fake images.
To stay safe, verify quickly before accepting any photo as genuine. In this post, we’ll teach you how to tell if pictures are fake by checking for manipulation signs, using metadata readers, running reverse searches, and applying forensic tools.
Need support after a scam? Join our community today.
How To Know If A Picture Is Fake?
Today, it’s common to face fake photos in social feeds, chat apps, and even emails linked to supposed transactions. One image pulled out of context can confuse people or support a scam. To stay safe, learn to spot visual signs and confirm where a photo came from:
1. Quick Cues And Context
Detecting a fake image requires paying close attention to subtle details, since manipulated photographs often contain visual errors that reveal the editing process. Recognizing these signs is the first step in avoiding falling for deceptions and in validating the authenticity of content shared on social networks.
Some features worth checking right away are:
- Reflections or shadows that do not match the scene.
- Irregular edges around objects or people.
- Hands or body proportions that appear altered.
- Text with inconsistent fonts or poor rendering.
- Duplicated elements within the same photo.
A helpful approach comes from OSINT (Open Source Intelligence), which focuses on comparing publicly available information. This method suggests checking:
- Origin: if the image comes from a legitimate source.
- Time: if the publication date matches the event it claims to illustrate.
- Other sources: if the image has been used before in different contexts.
Example
For example, during emergencies or conflicts, photographs that belong to past events are used. Applying these criteria helps verify if an image truly corresponds to the current situation or if it is being reused to spread false information.
2. Reverse Image Search
Reverse image search means uploading a photo to a specialized tool to track every place it has appeared online. This method allows you to check if a picture was published years ago or if it was altered to change its context.
Some of the most common uses include:
- Finding websites where the picture has been shared before.
- Spotting cropped, flipped, or edited versions.
- Checking when the image was first indexed online.
- Detecting abusive use in campaigns, fraud, or digital scams.
Example
A clear example came from photos circulated during recent political campaigns. Running a reverse search revealed that these pictures were linked to events from 2015, which helped expose the manipulation.
According to the Global Investigative Journalism Network (GIJN), the Reuters Institute found that 55% of internet users have seen misleading images online. Reverse search tools make it easier to check where a photo really comes from and stop the spread of edited or recycled pictures.
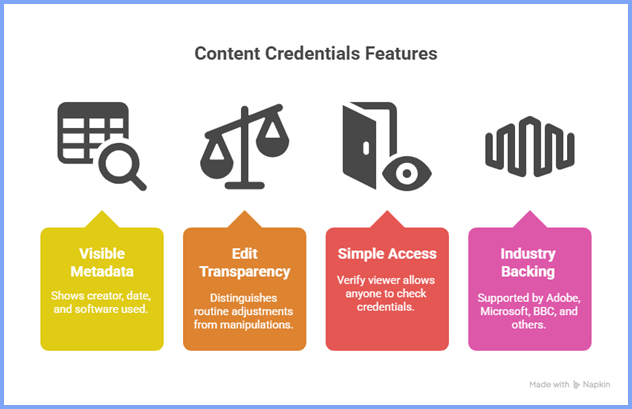
3. Content Credentials (C2PA)
Content Credentials (C2PA) is a way to see where an image came from and what was edited over time. Think of them as a digital history recorded inside the file, designed to add transparency in a world where answering how to know if a picture is fake gets harder by the day.
Some of the most common uses include:
- Showing who created the image and when.
- Recording the software used to edit it.
- Separating normal adjustments from edits made to deceive.
- Letting anyone view the data with a simple tool called Verify, an online viewer developed by the Content Authenticity Initiative.
- Being supported by big organizations like Adobe, Microsoft, and the BBC.
Example
A photo circulates online as proof of a recent hurricane. Checking it with Verify shows it was taken years earlier and edited with a specific program. Thanks to that record, it becomes clear that the picture is old and being shared out of context.
Discover how to remove your personal data and protect your privacy online.
Have questions about dealing with scams? Contact us for support.
Best Free Tools For How To Know If A Picture Is Fake Online
Figuring out if a photo is genuine or altered takes more than a quick look. You can use free options, reverse image search, metadata review, and digital forensics to spot edits, trace where a picture came from, and place it in the right context.
1. Google Images / Lens / About This Image
Google Images and Google Lens make this process accessible for how to know if a picture is fake. Upload a photo or capture it on your phone, then search for matches across the web.
In About this image section, you also see when the photo first shows up, which sites have posted it, and how it has moved online, useful details for testing authenticity.
Google Lens Advantages
- Simple on mobile and desktop.
- Finds the first known appearance of a picture.
- Lists pages that use the photo and helps compare versions.
- Includes Circle to Search for quick lookups on a phone.
- Works directly within Google, no extra apps needed.
Google Lens Disadvantages
- Can miss high-level edits from professional software.
- Very recent or little-shared images may show few results.
- Focuses on context, so technical manipulation details can be limited.
- History may be incomplete if sharing happened in closed networks or private groups.
2. Fact Check Explorer
Fact Check Explorer, part of the Google News Initiative, makes verifications from trusted media and fact-checking groups. It lets you confirm if a photo, video, or news item has already been reviewed. This makes it useful against misinformation related to crypto. It can even help in spotting cases linked to a Gemini scam.
The tool’s filters help you refine results by topic, region, or language, which is useful across different cultural or geographic settings. In practice, it’s a strong first stop to check if a viral image has been reviewed before by recognized fact-checkers.
Fact Check Explorer Advantages
- One place to find verifications, so you don’t have to scan many sites by hand.
- Includes recognized outlets and fact-checking groups, which builds trust in the results.
- Free, online, and no sign-up required.
- Shows the date and context of each verification, helping you judge how current it is.
Fact Check Explorer Disadvantages
- Only lists verifications that already exist, so very new images may be missing.
- Fresh stories can take time to appear, which limits their use in fast-moving situations.
- Geared more to articles and news than to deep technical analysis of images.
- The scope depends on participating organizations, so some languages or regions may have less coverage.
3. TinEye
TinEye is a well-established reverse image search engine. It compares a photo against a large index and returns matches that help you track where an image came from and locate alternate versions.
Unlike general search engines, TinEye focuses specifically on images, which makes it a good fit for people who want a targeted way to confirm how to tell if pictures are fake.
TinEye Advantages
- Fast results with detailed matches.
- A date sort helps surface the earliest known appearance.
- Browser add-ons for Chrome and Firefox support quick lookups without leaving the page.
- Useful for spotting reuse across sites and contexts.
- Free access, with paid options for higher-volume or advanced queries.
TinEye Disadvantages
- Very recent content may be missing from the index, so new images can be tougher to trace.
- Mobile integration is narrower than what you get with Google Lens and related tools.
- It does not reveal deep edits or internal changes (for example, Photoshop retouching).
- Because it is a matching tool, it works best alongside other methods for a fuller review.
4. Forensically
Forensically is a free tool for digital forensics that helps detect changes in photographs. Instead of searching the web for matches, it scans the image itself for its structure and compression to determine signs of editing.
A core feature is Error Level Analysis (ELA), which reveals compression differences and can point to areas that were altered. It does take practice reading the outputs, yet it’s a strong choice for digital investigations.
Forensically Advantages
- Filters for clone detection, edge analysis, and ELA.
- Free to use, no registration or installation required.
- Supports common formats like JPG, PNG, and TIFF.
- Works well with high-resolution images for precise review.
- Best for users with intermediate or advanced skills.
Forensically Disadvantages
- More time to learn than automated search tools.
- Results need careful reading to avoid false conclusions.
- No reference index like image-matching engines (e.g., Google Images, TinEye).
- The interface can be challenging for new users.
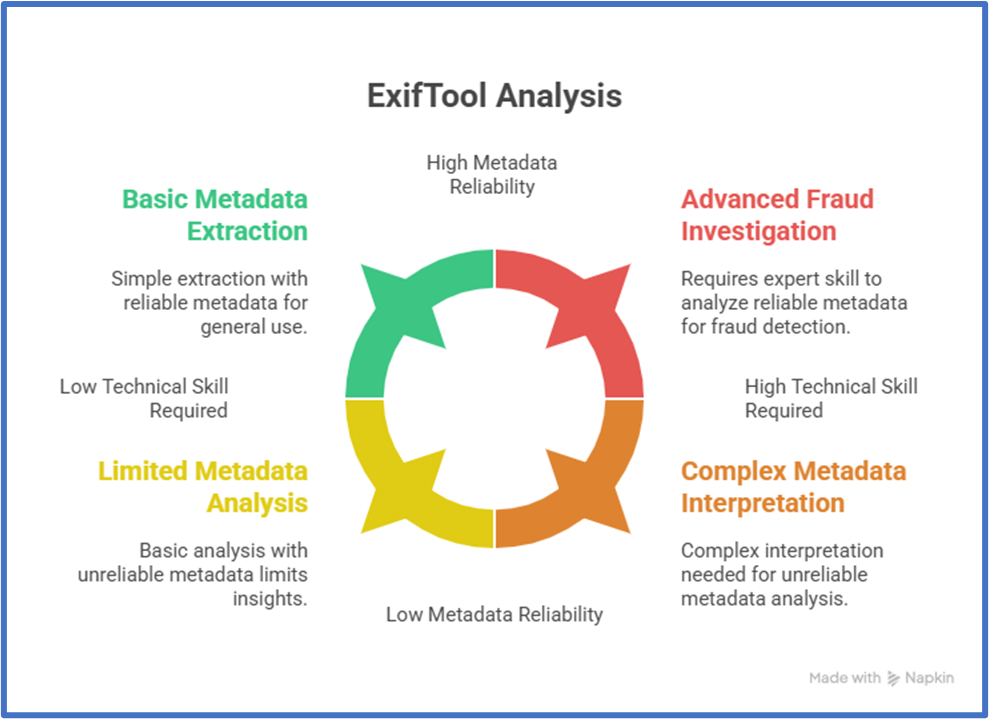
5. ExifTool
ExifTool is an advanced utility for extracting and reading EXIF metadata from images. These records can show when the photo was taken, which camera captured it, the GPS location, and the software used for edits.
To know if the picture is fake, metadata can uncover mismatches between what the image shows and the file’s technical record. This makes ExifTool especially valuable in online fraud investigations, where altered visuals are often tied to crypto-related cases, including schemes like a Bitcoin Code Scam.
ExifTool Advantages
- Broad technical detail: capture time, camera model, location, edit software, and more.
- Works on Windows, macOS, and Linux.
- Supports a wide range of image and video formats.
- Free and open source, with frequent updates.
- Useful for checking if a photo was altered or taken at a time different from the claim.
ExifTool Disadvantages
- Interpreting fields correctly takes technical skill.
- Many sites remove or change metadata on upload, which reduces what you can learn from the file.
- The interface is geared to the command line, which can be tough for first-time users.
- It won’t reveal visual edits by itself; combine it with other tools for a fuller review.
Explore Ways to Detect Fake Photos and Avoid Scams
Learning how to know if a picture is fake helps stop scams built on altered photos. Use reverse image search for reused visuals, metadata checks for inconsistencies, fact-check platforms for reviews, and forensic tools for hidden edits. Together, these methods make image verification more efficient.
At Cryptoscam Defense Network, support includes identifying fake receipts, spotting manipulated IDs, and tracking new fraud tactics like an Apple intelligence scam. Using these methods together gives you a clear way to verify images and act with trust.
We Want to Hear From You!
Fraud recovery is hard, but you don’t have to do it alone. Our community is here to help you share, learn, and protect yourself from future fraud.
Why Join Us?
- Community support: Share your experiences with people who understand.
- Useful resources: Learn from our tools and guides to prevent fraud.
- Safe space: A welcoming place to share your story and receive support.
Find the help you need. Join our Facebook group or contact us directly.
Be a part of the change. Your story matters.